HowTo: Let Fail2Ban automatically gather IP information
Fail2Ban allows the server administrator to have his access log files being automatically monitored for malicious behaviour. Often enough it’s interesting to see where the attack comes from geographically. And sometimes this helps identifying bugs with broken client software or wrong user authentication. Since my installation of Fail2Ban was unable to detect the public IP whois information, I tweaked the notification action command to load the missing data.
Fail2Ban is a tool for banning IP addresses via iptables, given by lists of logical rules and filters on log files. Click on the blog tag above to find an introduction.
Configuration
First check the configuration of Fail2Ban. Let’s assume, you have the default action with action_mwl enabled.
grep 'action = %(action_' /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf:action = %(action_)s
/etc/fail2ban/jail.local:action = %(action_mwl)s
Here the “Mail-WhoIs-Lines” action is enabled by default, meaning the admin will receive a mail with who-is information of any IP being banned, together with the affected log lines.
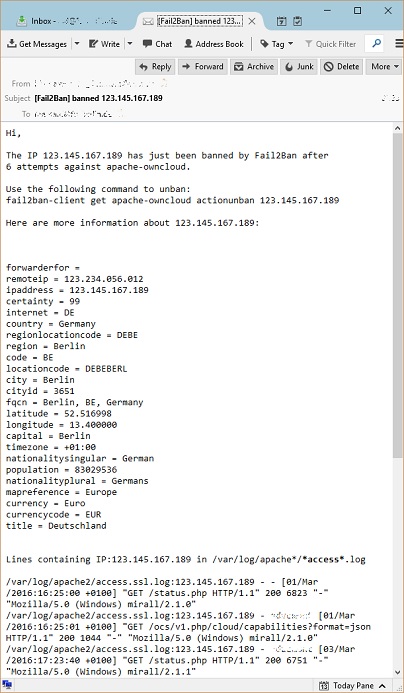
Improving the actionban command
The changes are straight forward:
- Greetings, IP, number of failures and jail name (default)
- Command to unban
- Standard output of system
whoiscommand - formatted JSON string from public geo API response
- Lines containing the IP (default)
vim /etc/fail2ban/action.d/mail-whois-lines.conf
actionban = printf %%b "Hi,\n
The IP <ip> has just been banned by Fail2Ban after
<failures> attempts against <name>.\n\n
Use the following command to unban:\n
fail2ban-client get <name> actionunban <ip>\n\n
Here are more information about <ip>:\n
` whois <ip> ` \n\n
` wget -qO- -t 5 http://getcitydetails.geobytes.com/GetCityDetails?fqcn=<ip> | sed 's/\",\"/\n/g; s/geobytes//g; s/\":\"/ = /g' | tr -d [{\"}] ` \n\n
Lines containing IP:<ip> in <logpath>\n
`grep '\<<ip>\>' <logpath>`\n\n
Regards,\n
Fail2Ban"|mail -s "[Fail2Ban] <name>: banned <ip>" <dest>
You can reload the Fail2Ban configuration with the usual service command.
service fail2ban reload
-or-
/etc/init.d/fail2ban reload